Sentiment Models
Once a model has been created, either empty or adding imported entries, you will be redirected to the model view. This is what you will see after creating a new model:
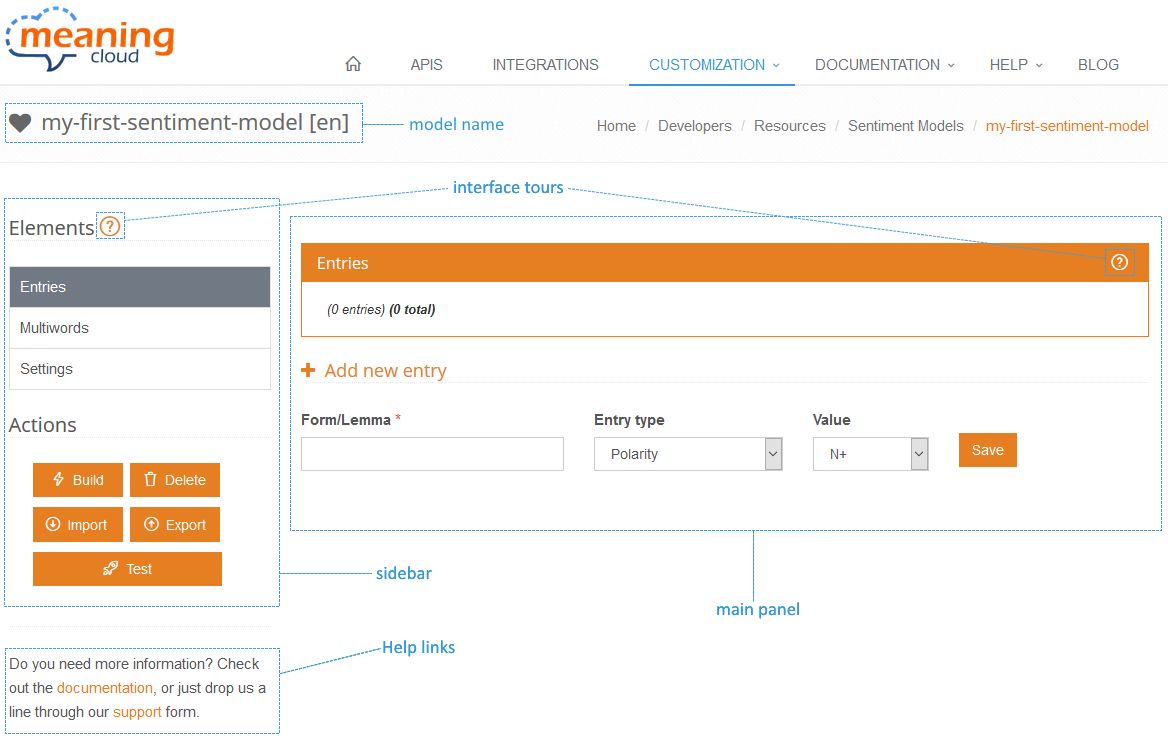
The structure of the sections that enable to interact with the different elements of a model will always be as follows. The view features a sidebar on the left where you can access to all the elements and actions available for the model, and a main panel dedicated to show the information of whichever element you are working on.
In the top right of the page, you find the name of the sentiment model, and below the sidebar, links to additional help.
Both the sidebar and the main panel feature a question mark: . By clicking on it, you will be given a tour of the element you've clicked on, explaining quickly and easily what its different parts are.
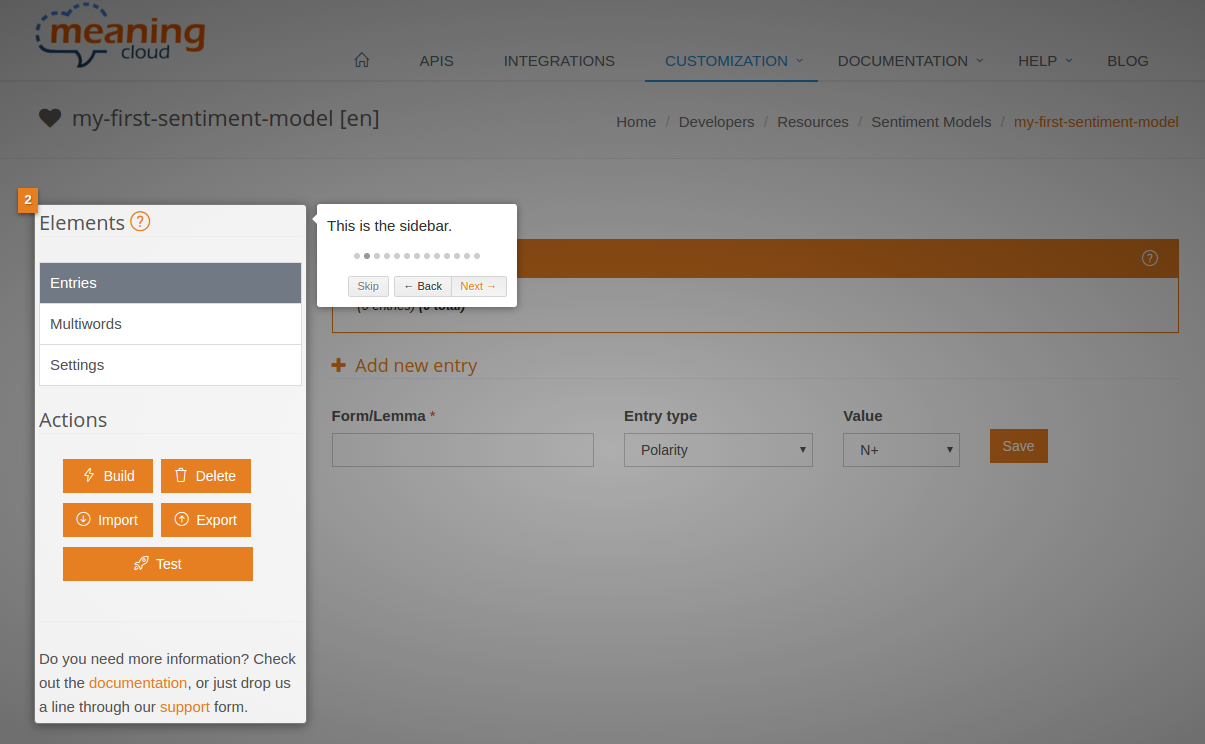
Sidebar
The sidebar is the same for all the different sections of the model view, so we will talk about it here. It is divided into two different parts: the elements that constitute the model and the actions you can perform.
Elements
The elements of a model are the configurable aspects available that enable to define how the model is going to work.
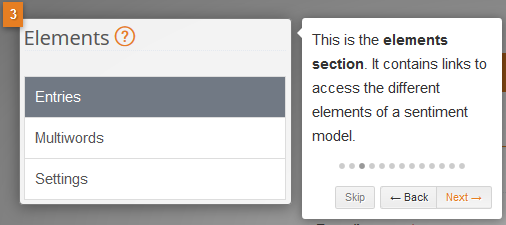
There are three elements:
- Entries: the word/s you are assigning a sentiment behavior to.
- Multiwords: combinations of words that if they appear in a specific order, are always grouped together.
- Settings: contains the basic configuration of the sentiment model, such as its name and description, etc.
Actions
The actions are the different operations that can be performed on a sentiment model.
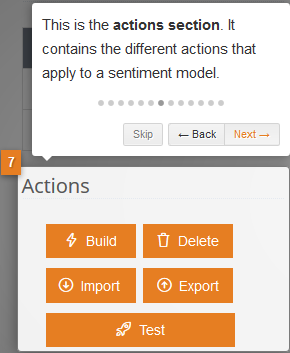
There are five possible operations:
- Build: checks if everything is defined correctly and ensures you test with the most recent version.
- Delete: removes the sentiment model and all its contents.
- Import: loads automatically entries into your model from a tsv file (tab separated values).
- Export: extracts the sentiment model.
- Test: tests the model’s functionality.

